An equipment maintenance schedule is a plan that outlines when and how often maintenance tasks need to be performed on specific equipment to keep it running smoothly. It helps businesses minimize unplanned downtime, save on repair costs, and extend the lifespan of their assets.
In this article, we’ll cover everything you need to know about creating an effective equipment maintenance schedule — what information to include, how to decide which equipment to prioritize, and different ways to schedule and track ongoing maintenance work.
Let’s dive straight in.
What should an equipment maintenance schedule include?
A proper equipment maintenance schedule will include all the basic details your team needs to plan and schedule maintenance work. This often includes:
- Equipment details: Name, ID number, location, and specifications of the equipment.
- Maintenance tasks: A clear description of each task to be performed, such as inspections, lubrication, part replacements, or cleaning.
- Task frequency: How often each task needs to be done (e.g., daily, weekly, monthly, based on usage, or condition-based).
- Required expertise: Can any technician do it, or does it have to be assigned to an electrician, pipefitter, etc.?
- Tools and resources: Any tools, parts, or manuals required to complete the tasks.
- Due dates: Specific dates or triggers (like usage hours or sensor data) for when the work is due.
- Completion records: A log to track when tasks are completed and any observations made during maintenance.
A well-organized maintenance schedule is a giant first step toward ensuring smooth operations at your facility.
Which equipment must be scheduled for maintenance?
Different types of equipment require different levels of attention. When deciding which assets to include in your preventive maintenance schedule, focus on the following:
- Critical equipment: Start with machinery that is essential to operations. Any breakdown of these assets can significantly disrupt production and incur high costs.
- High-usage equipment: Equipment that runs frequently or operates continuously is more prone to wear and tear and should be prioritized for regular maintenance.
- Manufacturer recommendations: Follow the guidelines provided in the equipment manuals. Manufacturers often specify the recommended maintenance intervals and tasks.
- Safety risks: Include equipment that, if not maintained, could pose safety hazards to workers or the facility.
- Maintenance history: Analyze past maintenance data to identify assets with recurring issues or frequent breakdowns.
You have to prioritize when you work with limited resources. Following these criteria will ensure your resources are allocated where they are needed most.
Ways to schedule equipment maintenance work
There are several ways to plan and schedule equipment maintenance, depending on your needs and resources. Let’s start with the simplest method and work our way up to more complex (and usually more effective) scheduling approaches.
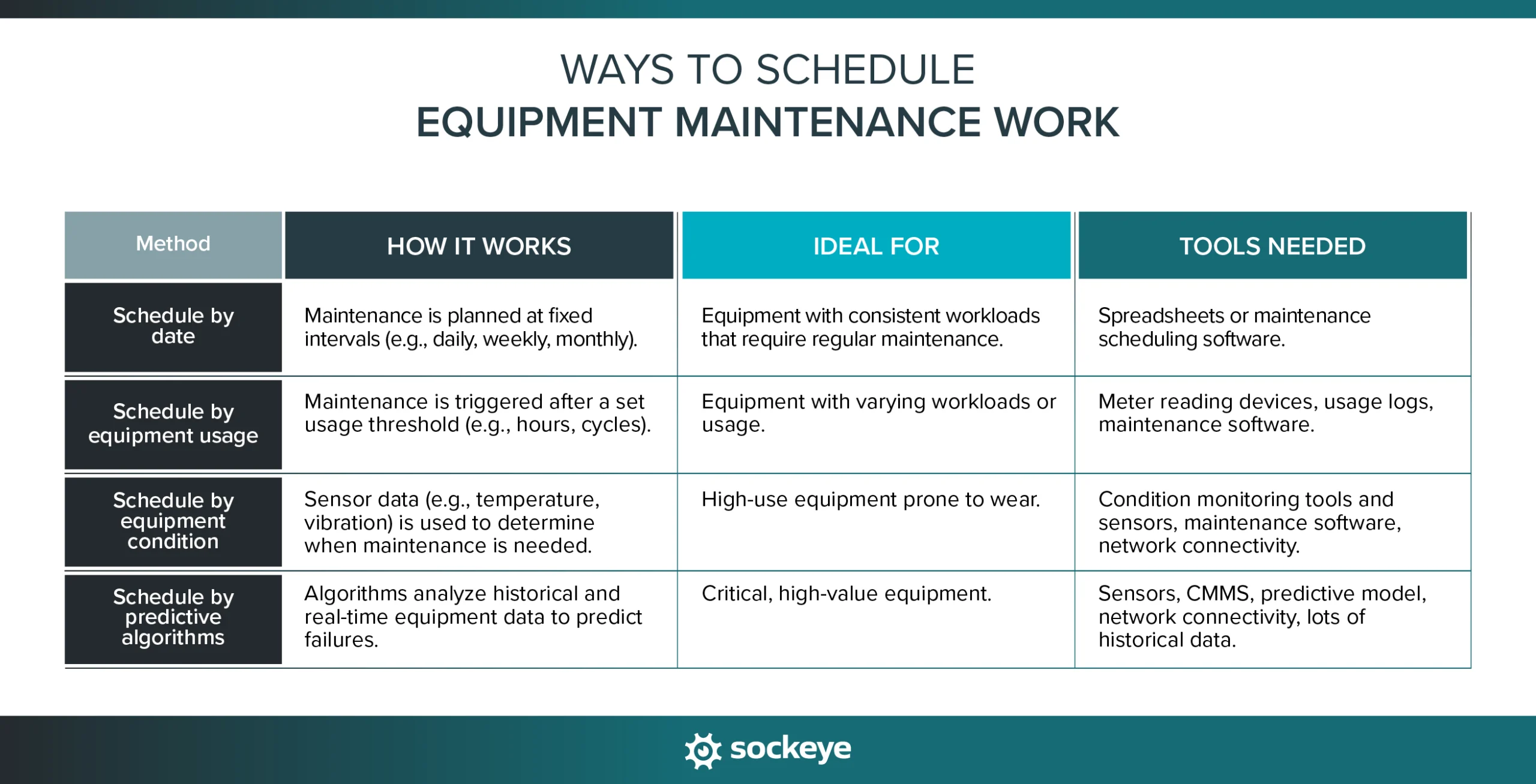
1. Schedule work by date
Scheduling maintenance work by date is the simplest and most common method. It involves planning tasks to occur at regular, pre-determined intervals, such as daily, weekly, monthly, or annually.
This approach is ideal for equipment with consistent workloads that require routine maintenance. For example, a manufacturing plant might schedule weekly lubrication for conveyor belts and monthly inspections for air compressors.
Calendar-based maintenance can be applied in two different ways:
- Fixed schedule: Maintenance tasks are performed on the same calendar date, regardless of whether the equipment was in use or when it was last maintained. This method is straightforward but can sometimes result in unnecessary maintenance.
- Floating schedule: Tasks are scheduled based on the completion of the last maintenance date. For example, if a monthly inspection is completed 10 days past the due date, the next inspection will happen one month after that last inspection was completed.
To implement calendar-based scheduling effectively, you’ll want to have:
- A spreadsheet or preventive maintenance scheduling software for assigning and tracking maintenance intervals and due dates.
- A calendar system (which usually comes with the scheduling software) to have a better overview of existing and upcoming work.
2. Schedule work based on equipment usage
Scheduling maintenance based on equipment usage involves planning work after a specific amount of usage hours, cycles, or production units. This approach ensures maintenance is more closely aligned with actual equipment wear and tear.
Usage-based scheduling is particularly useful for equipment with varying workloads, as it adapts to actual usage instead of fixed calendar dates.
For example, a company might schedule oil changes for a generator every 500 operating hours or replace a machine component after 10,000 production cycles. By tying maintenance to usage, teams can avoid both under-maintaining and over-maintaining equipment.
To implement usage-based scheduling effectively, you’ll need:
- Tools to track equipment usage, such as hour meters or production counters.
- Log sheets or digital systems to record usage data accurately.
- CMMS and maintenance scheduling software to automate reminders and task assignments based on usage thresholds.
3. Schedule work based on condition-monitoring data
Condition-based maintenance relies on (near) real-time data collected from sensors and monitoring tools to determine when maintenance is needed. By tracking specific parameters like temperature, vibration, pressure, or oil viscosity, you identify early signs of wear or malfunction and schedule maintenance accordingly.
Condition-based scheduling is ideal for equipment that operates continuously, experiences heavy use, or has components prone to wear — think motors, pumps, and rotating machinery.
For example, a sensor might detect abnormal vibrations in a motor, an early sign of potential bearing failure. Maintenance can then be scheduled before the issue escalates into a costly breakdown.
To implement condition-based scheduling effectively, you’ll need:
- Oil test kits, infrared cameras, vibration sensors, and other condition monitoring tools to track equipment health.
- A network connection (WiFi or wired) to transfer sensor data to your CMMS. Alternatively, you can take sensor readings manually every few days and type the data into your CMMS.
- CMMS to centralize sensor data and trigger alerts.
- Maintenance scheduling app to schedule maintenance work. While you can do this inside a CMMS, many teams find it difficult and cumbersome — they prefer to use a standalone scheduling app like Sockeye.
4. Schedule work based on predictive algorithms
Predictive maintenance uses advanced algorithms and machine learning to analyze historical data, equipment usage, and real-time performance metrics to predict when maintenance will be required. In the 2021 Plant Engineering research, 40% of facilities reported using some form of predictive maintenance.
Predictive maintenance scheduling is best suited for critical and high-value equipment where unexpected failures can lead to significant costs or downtime.
For example, predictive algorithms might analyze trends in temperature, pressure, and vibration to forecast when a pump is likely to fail. Maintenance work can then be scheduled just before failure is predicted, avoiding unexpected breakdowns while maximizing equipment uptime.
To implement predictive scheduling effectively, you’ll need:
- Condition monitoring sensors to collect performance data in real time.
- Data scientists or a third party to help you build and implement your predictive maintenance model.
- A lot of historical equipment performance and failure data to train and refine predictive algorithms.
- CMMS to centralize data, forward it to your predictive model, and trigger tasks based on the outputs of that model.
- A strong network connection to connect all of these sensors and systems.
Steps for creating an equipment maintenance schedule
Creating an equipment maintenance schedule involves three basic steps:
- Select equipment: Identify the assets that need to be included in your maintenance schedule based on their criticality, usage, and risk factors.
- Identify tasks: Determine the specific maintenance tasks required for each piece of equipment, such as inspections, part replacements, or cleaning.
- Set maintenance frequency: Establish how often each task needs to be performed, whether it’s time-based, usage-based, condition-based, or predictive.
When done, the only thing left is for the maintenance planner and scheduler to allocate resources, set due dates, and start assigning work to qualified personnel.
Here is a simplified example of an equipment maintenance schedule for a generator:
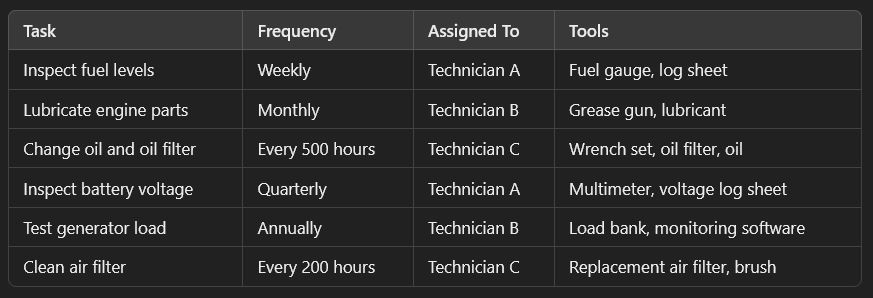
Most of this looks simple to do on paper. In practice, maintenance teams face all kinds of limitations — lack of labor, constant breakdowns, limited budget, etc. — that can make proactive equipment maintenance scheduling quite challenging.
If you’re experiencing similar issues, we share helpful advice that can make you more efficient in the following articles:
- Maintenance Planning Done Right: Steps and Best Practices
- Maintenance Scheduling Done Right: 11 Industry Best Practices
How to keep track of equipment maintenance
We have seen teams track equipment maintenance work in all kinds of ways — from paper-based systems and whiteboards to Microsoft Outlook combined with Excel spreadsheets to modern CMMS solutions.
These days, it is hard to make an argument for any system that isn’t digital. For any medium or large maintenance team, CMMS seems like the best bet for tracking and organizing ongoing equipment maintenance work. It will help you streamline workflows, track costs, and store records in one centralized location.
And if you find the scheduling functionality inside your CMMS too complex, you can always connect that CMMS to Sockeye and use our intuitive scheduling interface instead.
Streamline equipment maintenance scheduling with Sockeye
Sockeye is a simple but powerful app designed to simplify equipment maintenance scheduling. How does it achieve that?
For starters, Sockeye makes building effective schedules fast and easy. With our easy-to-use interface and automation features, you can create weekly and daily schedules in minutes, without needing extensive training.
Furthermore, Sockeye can integrate your existing CMMS and workforce management software. This means you will always know exactly who’s available, what tasks need attention, and what is the work in progress. If there is an emergency, schedulers can easily search, filter, and update the schedule while providing the entire facility with a live, verified schedule.
Here’s a 90-second video that explains how Sockeye simplifies the scheduling process:
Want to see how Sockeye would fit into your facility? Schedule a quick demo today and our team will show you how it can transform your maintenance scheduling workflows.