In maintenance, efficiency and productivity aren’t just buzzwords — they’re critical to ensuring smooth operations, reducing costs, and avoiding unexpected downtime. High-performing maintenance teams don’t just keep things running; they do it in a way that maximizes output while minimizing wasted time and resources.
But achieving and maintaining top efficiency is easier said than done. From complex schedules to equipment breakdowns, teams face a range of challenges that can derail even the best-laid maintenance plans.
To help you achieve excellence, this article will outline practical ways to measure and improve maintenance efficiency and productivity.
The relationship between maintenance efficiency and maintenance productivity
When discussing maintenance performance, efficiency and productivity go hand in hand. However, they aren’t one and the same:
- Maintenance efficiency measures how well resources — like time, labor, and materials — are used to complete maintenance tasks. High efficiency means tasks are completed with minimal waste and effort.
- Maintenance productivity focuses on output. It measures how much work is completed within a specific time frame or how effectively resources produce desired results.
The two are deeply connected. For example, a highly efficient team that wastes no time on unnecessary steps is more likely to be productive. At the same time, a focus on productivity — ensuring work gets done at a steady pace — often requires improving processes to boost efficiency.
To maximize performance, maintenance managers need to strike a balance between the two. Lean too heavily on one without addressing the other, and the entire operation can suffer. For instance, a team focused only on speed might rush through tasks, leading to mistakes and rework, ultimately hurting both efficiency and productivity.
By understanding how these concepts overlap and influence each other, you can create a maintenance strategy that’s not just good on paper but highly effective in practice.
How to measure maintenance efficiency and productivity?
Before you can improve maintenance efficiency and productivity, you need to measure them. After all, you can’t fix what you don’t understand. By tracking key metrics and analyzing trends, you can gain insights into what’s working, what isn’t, and where to focus your efforts.
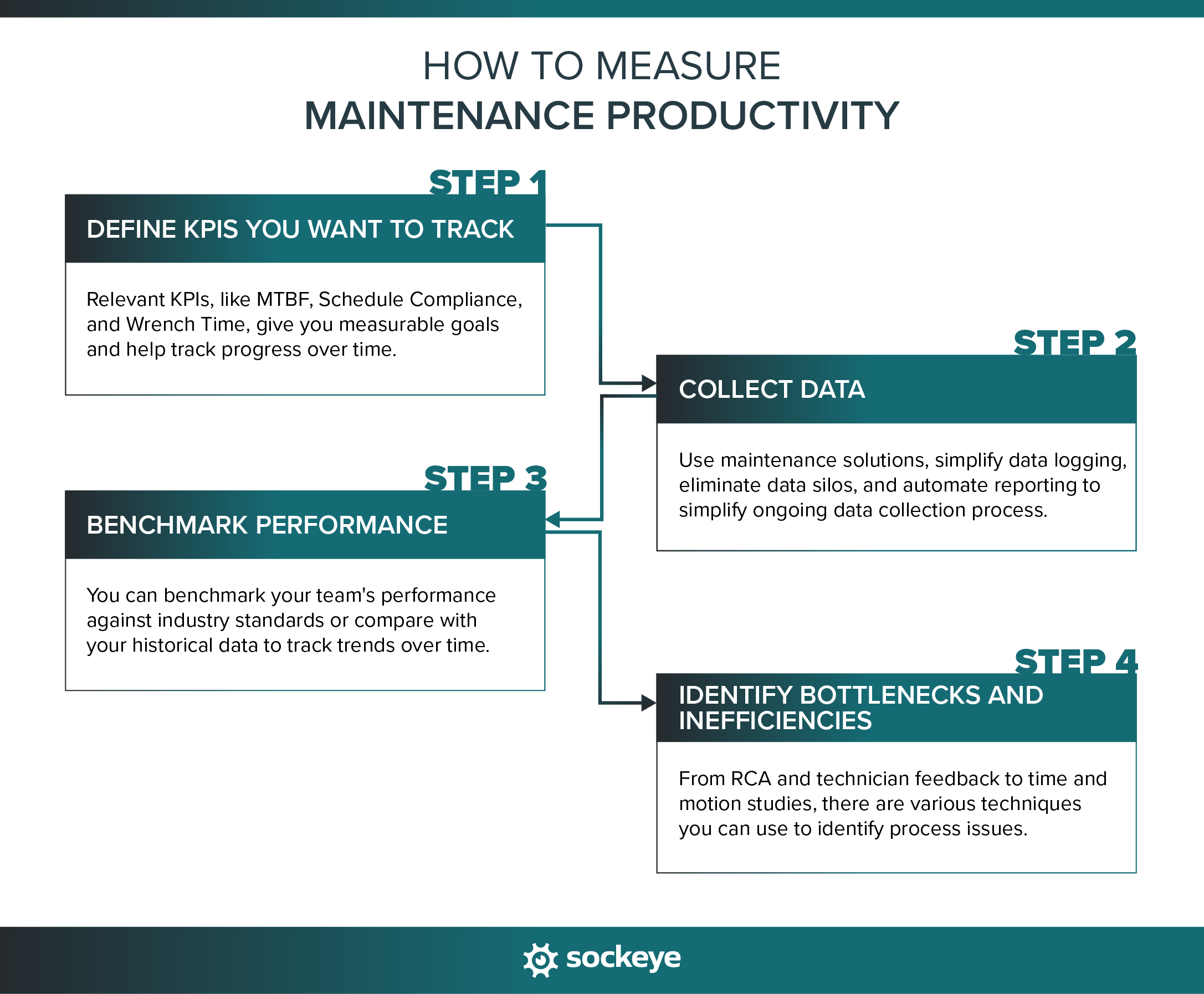
Step 1: Define KPIs you want to track
Key performance indicators (KPIs) give you measurable goals and help track progress over time.
Here are some common KPIs to consider:
- Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF): Tracks the average time equipment operates before failing. It helps assess the reliability of assets and the effectiveness of your maintenance plan.
- Mean Time to Repair (MTTR): Measures how quickly your team can restore equipment after a failure. Lower MTTR indicates faster problem resolution and improved productivity.
- Schedule Compliance: Tracks how much of your planned maintenance schedule is completed on time. This metric highlights your team’s ability to stick to the plan and avoid delays.
- Available Hours Used: Tracks the percentage of available maintenance hours scheduled during a week. The higher that percentage is, the more work you were able to schedule — which directly reflects your team’s overall productivity.
- Wrench Time: Measures the percentage of time technicians spend actively working on tasks versus waiting for tools, instructions, or parts. Improving wrench time is key to boosting efficiency.
- Maintenance Excellence Index (MEI): A comprehensive metric that combines multiple aspects of maintenance performance — such as planned vs. reactive maintenance, downtime, and work quality — into a single score. The MEI gives you a bird’s-eye view of how well your maintenance program is functioning overall and helps identify areas needing attention.
It’s important to tailor KPIs to your specific industry and organizational goals. For example, in manufacturing, you might focus on minimizing downtime and maximizing uptime, while in facilities management, you might track tenant service requests and response times.
By clearly defining KPIs that align with your objectives, you’ll lay the groundwork for collecting more meaningful and actionable insights.
Step 2: Collect data
Once you’ve identified the KPIs you want to track, the next step is to gather the data needed to measure them. The good news is that technology makes it easier than ever to collect accurate information without drowning in administrative work.
Here are some practical ways to streamline data collection:
- Use maintenance software: Solutions like CMMS, EAM software, and Sockeye can automatically track different metrics, such as work order completion times, labor hours, and downtime. This eliminates the need for manual record-keeping and ensures consistency.
- Simplify data logging: Make it easy for technicians to log work, track parts usage, and report issues directly from the field. This reduces paperwork and ensures data is captured promptly and accurately.
- Integrate systems: If your organization uses multiple platforms for maintenance, production, or operations, try to integrate them as much as possible. Unified systems provide a clearer picture of maintenance efficiency and productivity without requiring data entry in multiple places.
- Automate reporting: Set up automated reports to pull and summarize data from your systems. This saves time and makes it easy to monitor trends without spending hours generating spreadsheets manually.
The more streamlined and reliable your data collection process, the easier it will be to analyze and use the insights effectively.
Step 3: Analyze trends and benchmark performance
Here’s how you can approach this step effectively:
- Compare against historical data: Is your MTBF improving or declining? Are safety incidents becoming more or less frequent? Is your backlog growing or reducing? Tracking progress over time gives you a baseline to measure success and identify recurring problems.
- Benchmark against industry standards: Compare your KPIs to industry benchmarks or standards. This can provide valuable context about how your maintenance team is performing relative to peers. For example, if your wrench time is lower than the industry average, it could indicate inefficiencies in task execution or resource availability.
- Use visualizations: Charts, graphs, and dashboards make it easier to spot trends and understand complex data at a glance. Most maintenance platforms include built-in reporting tools to help you visualize your data quickly.
- Identify patterns: Analyze your data to detect recurring issues or opportunities for improvement. For instance, frequent downtime for a specific machine might point to the need for a more robust equipment maintenance schedule.
By comparing performance against historical data and benchmarks, you’ll gain a clearer understanding of where your maintenance team excels vs. where adjustments are necessary.
Step 4: Identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies
Some KPIs will undoubtedly be below your expectations. You will want to dive deeper into those to pinpoint bottlenecks and inefficiencies that are holding your team back.
After all, addressing these issues can lead to significant improvements in both maintenance productivity and efficiency.
Here are some practical ways to identify problem areas:
- Conduct Root Cause Analysis (RCA): For recurring issues, dig deep to uncover the underlying causes. Tools like the “5 Whys” method or Fishbone Diagrams can help structure this process.
- Evaluate resource utilization: Look at how time, labor, and materials are being used. Are technicians spending too much time waiting for parts or approvals? Are tools being misallocated? Improving resource allocation can eliminate unnecessary delays.
- Analyze workflows: Map out your maintenance workflows to identify bottlenecks. For example, if work orders frequently get stuck in the approval phase, streamlining that process could speed up task completion.
- Monitor equipment-specific data: Pinpoint underperforming assets by analyzing metrics like downtime, MTBF, and MTTR. Focus on the equipment that consistently underperforms or requires frequent repairs.
- Collect feedback: Ask your maintenance team about challenges they encounter during their daily work. Technicians often have valuable insights into inefficiencies that aren’t visible in reports.
For more advanced analysis, consider techniques like time and motion studies (observe and document how technicians perform tasks to identify unnecessary steps or inefficiencies) or maintenance simulation tools (use software to simulate maintenance scenarios and test potential process changes in a virtual environment before implementing them in real life).
Tried and tested ways to improve productivity and efficiency
Identifying inefficiencies is just the beginning—now it’s time to take action. Boosting maintenance productivity and efficiency often requires a combination of strategic planning, process improvements, and leveraging the right tools.

1) Address the most common “killers” of productivity
Productivity doesn’t disappear overnight — it’s often eroded by a handful of recurring issues that go unnoticed for far too long.
Here are the usual suspects:
- Poor planning and scheduling: Without clear plans or effective scheduling, maintenance tasks can quickly become chaotic. Make sure your team follows maintenance planning and scheduling best practices.
- Lack of communication: Miscommunication between team members or departments can lead to delays, repeated work, or missed tasks. When maintenance teams don’t have clear instructions or updates, productivity suffers.
- Insufficient training: Untrained or undertrained technicians often spend extra time troubleshooting issues or relying on others for help. This not only slows work but also increases the likelihood of errors.
- Resource unavailability: Delays in accessing tools, spare parts, or machines can leave technicians idle and frustrate efforts to complete tasks on time.
- Reactive maintenance overload: If your team is constantly reacting to unexpected breakdowns, they can’t focus on preventive or planned maintenance tasks, leading to a downward spiral of inefficiency. More proactive strategies, like predictive maintenance, can lead to a 55% increase in maintenance staff productivity.
By targeting these productivity killers head-on, you can create a more organized and efficient maintenance operation.
2) Balance your maintenance effectiveness ratio
The Maintenance Effectiveness Ratio (MER) essentially tells you how much time are you spending on proactive maintenance compared to reactive maintenance. A healthy MER leans heavily toward proactive work.
You can use your CMMS or maintenance logs to calculate the proportion of proactive vs. reactive tasks. Aim for a ratio that aligns with your industry and equipment needs. For many organizations, a proactive ratio of 70-90% is a good benchmark.
While prioritizing proactive maintenance is ideal, it’s possible to overdo it — spending time maintaining equipment that doesn’t require immediate attention. You can look at other metrics like MTBF and maintenance costs to spot if you might be over maintaining some assets.
3) Standardize maintenance tasks and process
One of the most effective ways to improve both efficiency and productivity in maintenance is to standardize how tasks are performed. You can do that by:
- Creating Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Develop clear, step-by-step instructions for common maintenance tasks. These should include everything from safety protocols to troubleshooting steps to simple inspections.
- Use checklists: Provide technicians with task-specific checklists to ensure nothing is missed during maintenance.
- Implement Work Order templates: Standardize your work order format with fields for critical details such as task descriptions, priority levels, and required resources.
- Document best practices: Gather insights from your most experienced technicians and document their methods for handling challenging maintenance tasks. Share these best practices across your team.
- Streamline tools and equipment: Standardize the tools and equipment used for maintenance tasks to reduce downtime caused by searching for or swapping out the wrong tools.
Many of these tasks will take some time to execute. However, once done, they will create a strong foundation for improved efficiency and productivity — while only needing an occasional update.
4) Train and develop your workers
This point is pretty much self-explanatory. The more skilled your team is, the more efficient it can be.
When appropriate, help technicians develop cross-functional skills, provide leadership training for team leaders, and make sure that everyone knows how to use the tools and technology they need to interact with (CMMS, IoT sensors, predictive software, new welding machine, etc.).
Start by identifying skill gaps within your team and developing training plans to address them. There is a great thought in this article on manufacturing management that goes:
“Build the habits of success before you have to, so you never get to the place where you have to.”
In other words, do not wait for training to become a grave necessity.
5) Set priorities and optimize scheduling
Poor scheduling, conflicting priorities, or last-minute changes can disrupt workflows, cause delays, and lead to burnout for your maintenance team.
Furthermore, prioritizing critical tasks ensures that your team focuses on the work that has the most significant impact on operations, safety, or compliance. Low-priority tasks can be deferred, scheduled during less demanding times, or grouped with other work for efficiency.
We have a detailed guide on maintenance scheduling if you wish to dive deeper into this topic.
6) Improve internal and external communication
Poor communication between team members or departments (especially Operations) can lead to delays, misunderstandings, and wasted effort.
Here are some tips to improve communication:
- Use team collaboration tools: Equip your team with tools like Slack, Microsoft Teams, or maintenance software that can share updates, assign tasks, and provide real-time feedback.
- Hold regular meetings: Daily or weekly check-ins allow teams to discuss priorities, address issues, and plan upcoming tasks together.
- Create clear channels of communication: Establish clear protocols for reporting problems, escalating issues, or sharing updates. For example, use a dedicated channel for urgent maintenance alerts.
- Collaborate with operations: Ensure that maintenance schedules align with production needs to minimize disruptions. Open communication about production plans or equipment usage can help maintenance teams plan better.
- Develop a feedback loop: Encourage feedback from other departments on how maintenance can better support their needs. Likewise, share insights with them about how their actions impact maintenance efficiency.
Investing in better communication — whether through tools, processes, or training — can have a dramatic impact on productivity and efficiency.
Boost maintenance productivity with Sockeye
Sockeye is a simple maintenance scheduler designed to take the complexity out of maintenance scheduling.
From real-time insight into technician availability to weekly/daily scheduling automation to giving everyone a live, verified schedule, Sockeye helps maintenance teams schedule more work — so they can get more work done.
For example, Sockeye makes it easy to load the schedules to 100% of technician availability, which helps our clients increase productivity by up to 50%!
Furthermore, you can leverage our delay codes functionality to track and minimize delays, you can set and track various productivity-related KPIs, you can visualize your maintenance schedules to communicate priorities and keep everyone on the same page, and much more.
Here is a quick overview of Sockeye for those interested in learning more.
Sockeye is a perfect solution for organizations that have a CMMS but are not satisfied with its scheduling functionality. You can integrate Sockeye with your CMMS and use our intuitive scheduling interface instead.
Book a quick demo with our team and let’s boost your productivity with better scheduling.