Tired of unexpected equipment failures throwing a wrench in your operations? Preventive maintenance can be the solution you are looking for.
In order to make it work, you need two things: a clear preventive maintenance plan for important assets and a solid preventive maintenance program to manage the big picture.
In this article, we’ll break down the difference between the two, share a simple three-step process for creating a PM plan, and highlight tools to build a program that keeps your team one step ahead.
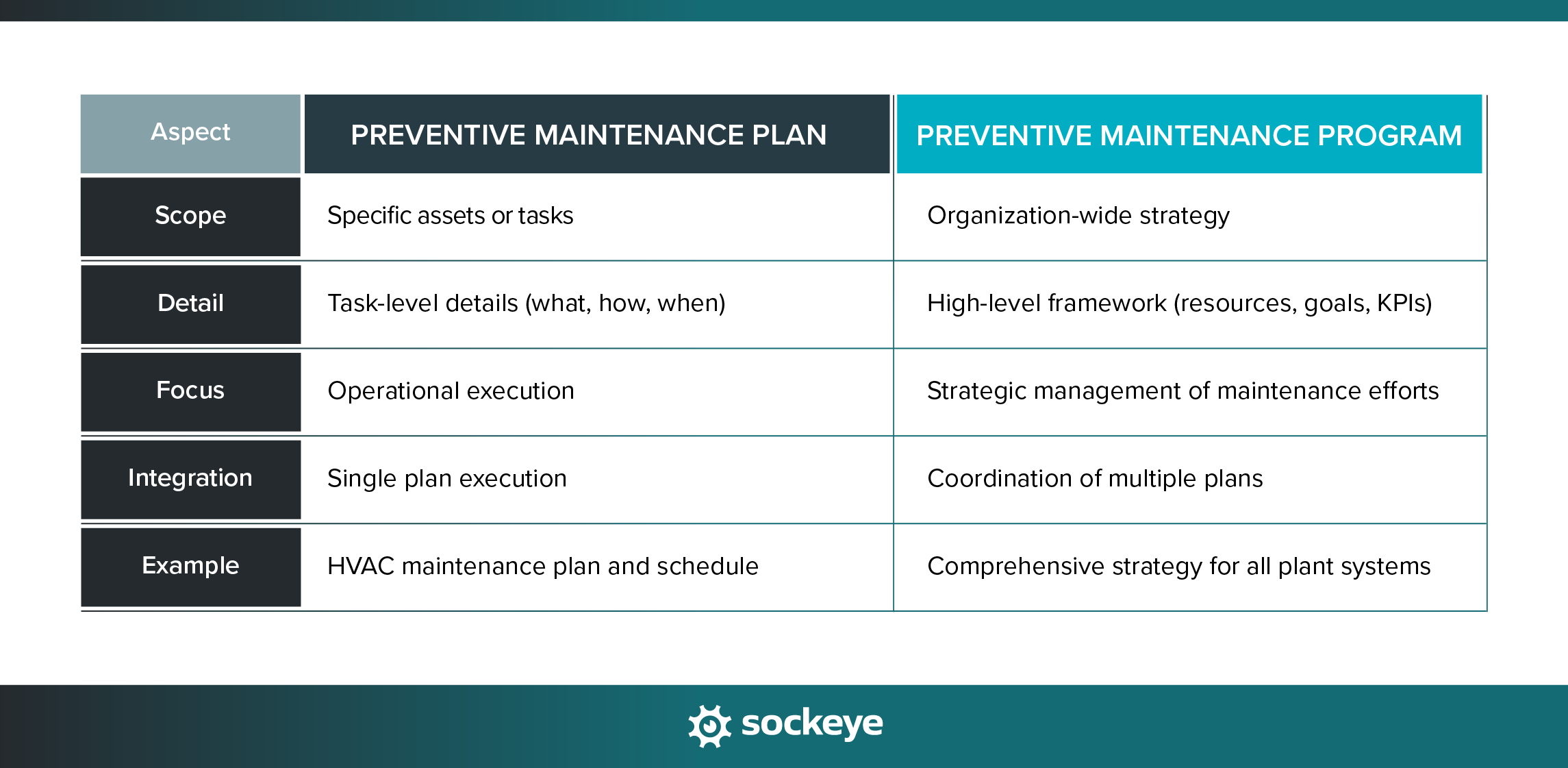
The difference between a PM plan and a PM program
Even though these two terms are often used interchangeably, it’s useful to know the difference.
A preventive maintenance program is a framework for implementing preventive maintenance across an entire organization or facility. It often includes policies, resources, goals, and management strategies to ensure maintenance plans are successfully executed.
A preventive maintenance plan is a strategic document outlining the what, when, and how of preventive maintenance. It is typically a smaller-scale, detailed roadmap focused on specific assets, tasks, and schedules.
To use a cooking analogy:
- PM plan = A recipe for maintaining specific equipment.
- PM program = A kitchen operation managing all recipes, staff, tools, and goals to keep everything running smoothly.
In practice, an effective preventive maintenance program consists of multiple preventive maintenance plans for individual assets or systems. Together, they form a proactive approach to minimizing downtime, extending equipment lifespan, and reducing operational costs.
Creating a preventive maintenance plan in 3 simple steps
Creating a preventive maintenance plan doesn’t have to be complicated. To keep things actionable, here’s how to create a preventive maintenance plan for an asset in just three steps.
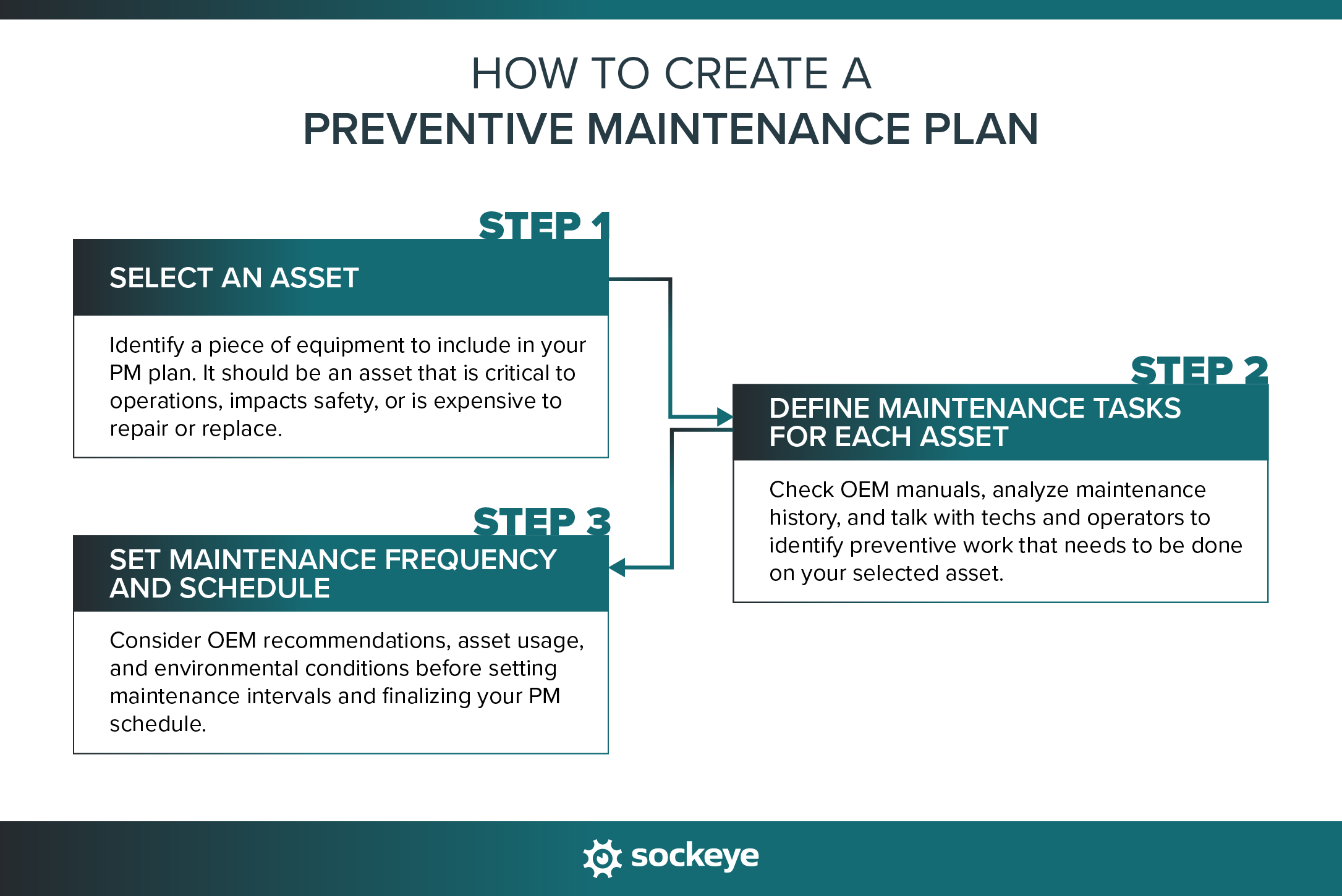
1. Select an asset you want to include in your PM plan
To start, you need to identify which equipment to include in your preventive maintenance plan. Focus on assets that:
- Are critical to production or operations
- Have a significant impact on safety or compliance
- Carry high costs of failure or replacement
Some maintenance departments will have their asset information spread out across multiple spreadsheets or filing cabinets. If you are in the same boat, start with an asset inventory check. The goal is to have an up-to-date list of assets in one place, along with basic details like model, age, location, maintenance history, and manufacturer recommendations.
If you are on the fence about some assets, consider performing a criticality analysis.
Quick example: Imagine you’re working in a manufacturing facility. One of your key assets is a conveyor belt system responsible for moving products between workstations. This equipment is critical to production, and any downtime causes delays. You’d include this conveyor belt in your PM plan, noting the basic equipment details we mentioned earlier.
In general, it’s a good idea to prioritize critical or problematic assets — you’re going to see larger positive effects of having them in a PM plan (effects you can later leverage to expand your preventive maintenance program).
2. Define maintenance tasks for each asset
Once you’ve identified and prioritized your assets, the next step is to figure out exactly what needs to be done to maintain them. Here’s how to approach this:
- Refer to OEM manuals: Start with the manufacturer’s guidelines for the asset. These manuals often include recommended tasks, maintenance intervals, and procedures.
- Analyze past failures: Look at historical maintenance records to identify recurring issues or failure points. Use this information to prevent similar problems in the future.
- Talk to technicians and operators: The people who interact with the equipment daily — like technicians and machine operators — often have valuable insights into equipment condition and recurring problems.
With that information, you should be able to build a detailed list of maintenance activities for each asset in your preventive maintenance plan. These lists often include:
- Inspections: Checking belts, hoses, or electrical connections for wear and damage.
- Cleaning: Removing dust, debris, or buildup that could impact performance.
- Lubrication: Applying grease or oil to reduce friction and prevent wear.
- Part replacements: Replacing filters, belts, bearings, or other components.
Example: The image below shows a list of potential PM tasks for a conveyor belt system. Let’s also mention that the frequency, if you include it at this stage, can be just what the OEM recommends. You will need to account for other things before finalizing the schedule.

3. Set maintenance frequency and schedules
After identifying the tasks for each asset, it’s time to determine how often they need to be performed. To set an effective preventive maintenance schedule, consider the following:
- Follow manufacturer recommendations: The OEM manuals provide a solid baseline for maintenance intervals. Use these as a starting point.
- Consider asset usage: Frequency can vary depending on how often the asset is used. The more it is used, the more preventive maintenance it needs.
- Account for environmental conditions: Assets operating in harsh environments (e.g., dusty, humid, or high-temperature settings) may require more frequent maintenance.
- Choose the right scheduling method: You can schedule tasks based on fixed intervals (e.g., weekly, monthly, annually) or asset runtime (e.g., every 500 hours of operation or 1,000 cycles). Use the table below to see the best use cases for both methods.
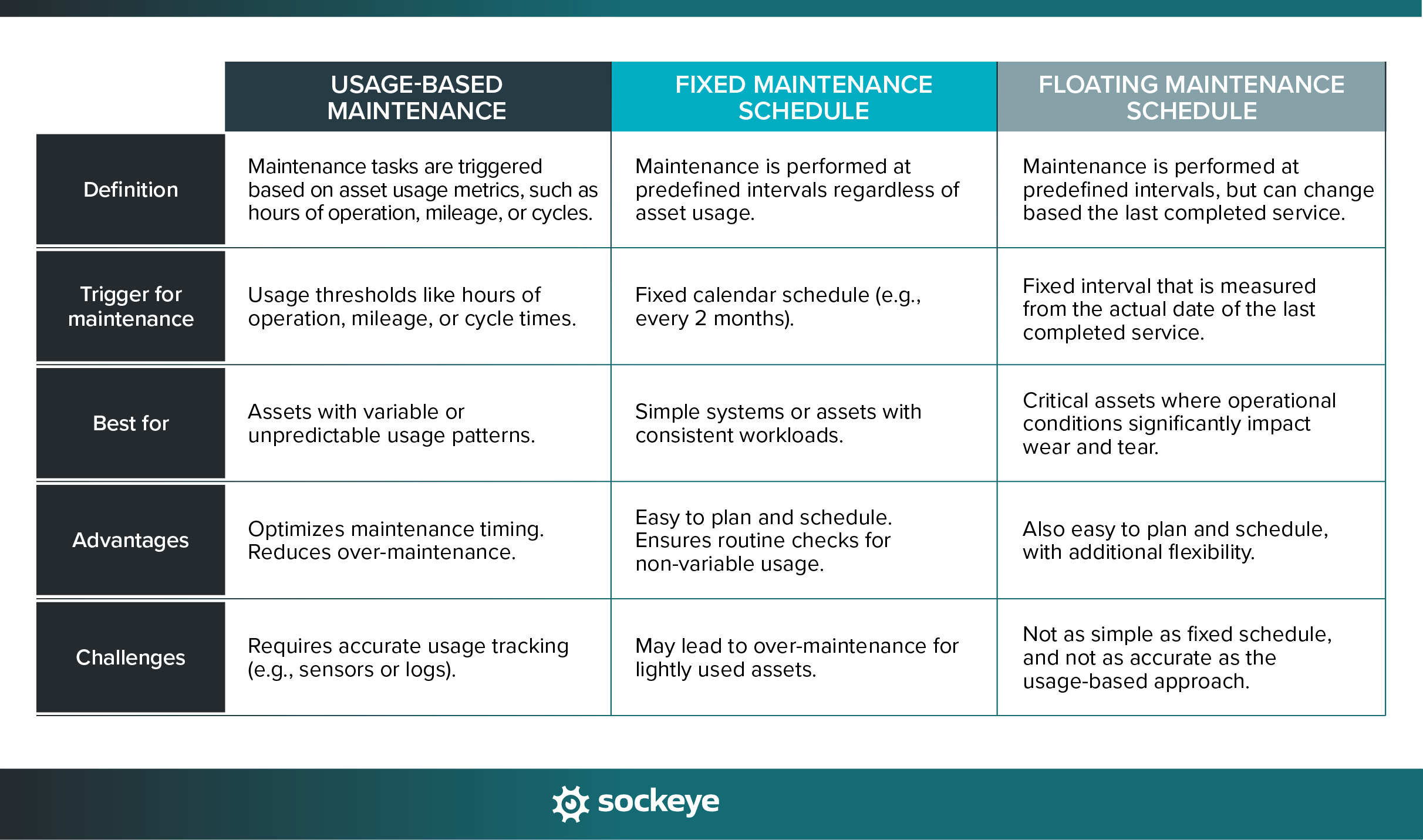
If you have multiple assets in your preventive maintenance plan, your PM schedule could look something like this:
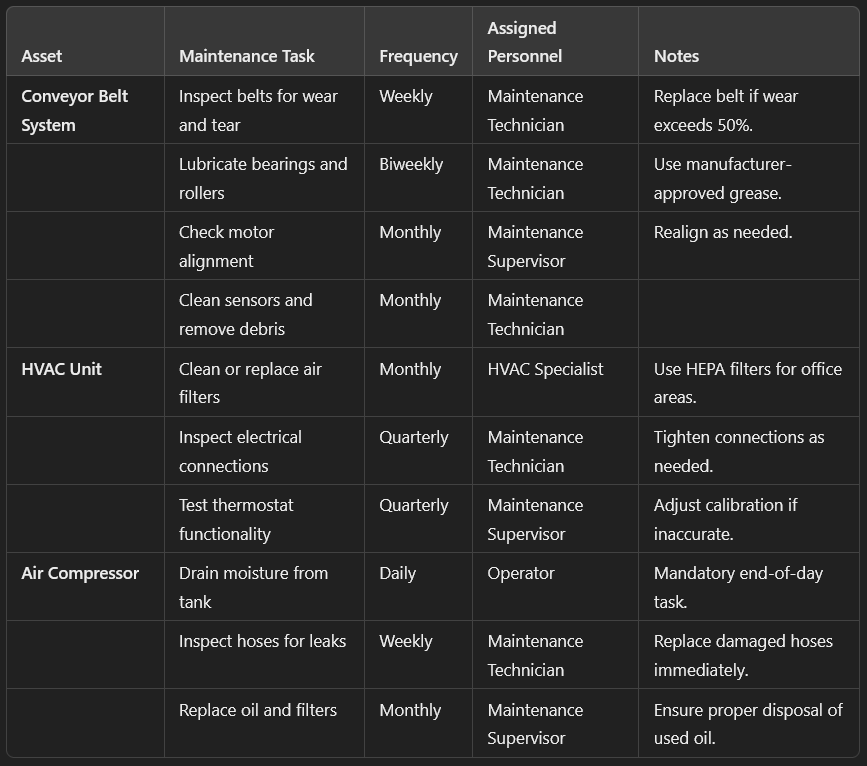
Ideally, you would have the schedule visualized inside your CMMS software and use a preventive maintenance scheduling app like Sockeye to simplify the scheduling process and stay on top of preventive work. Alternatively, smaller maintenance teams could get by using a preventive maintenance schedule template built with Excel or Google Sheets.
It’s important to note that labor resources are often a limiting factor in executing preventive maintenance effectively. 41% of facilities cite a lack of resources or staff as a major challenge to improving their maintenance programs. This makes careful planning — and workload balancing — a critical component of your PM strategy.
4. Create SOPs and checklists for recurring tasks (optional)
Creating maintenance plans is the easy part — making sure your team sticks to them is where your preventive maintenance program will fall or succeed. And the leaders over at Dynaway EAM agree with us:
“Effective planning and scheduling play a crucial role in the ultimate success of any preventive maintenance program.”
So, to help with planning, prioritization, and scheduling of day-to-day work, take a look at other in-depth guides on our blog:
- Maintenance Planning Done Right: Steps and Best Practices
- Maintenance Scheduling Done Right: 11 Industry Best Practices
- How To Prioritize Maintenance Work Orders
Another thing that we recommend is creating standard operating procedures (SOPs) and preventive maintenance checklists. Both help improve the efficiency, safety, and quality of recurring maintenance work. You can include step-by-step instructions, tools required, and safety precautions.
Below is an example of a preventive maintenance checklist for a conveyor belt inspection.

How to ensure the success of your preventive maintenance program
Making your preventive maintenance program a success requires paying attention to the following factors:
- Setting clear goals and KPIs: Define what success looks like (e.g., reduced downtime, fewer breakdowns, or lower maintenance costs).
- Getting upper management support: Ensure leadership is on board to provide resources, tools, and time.
- Training and empowering your team: Equip your technicians with the knowledge and tools they need to execute maintenance tasks effectively.
- Tracking and optimizing performance: Use data to monitor progress, adjust schedules, and continuously improve your program.
Most maintenance teams will want to start small. Choose a few critical assets and make sure they are maintained proactively. This way, you will be able to sort out the kinks in your planning and scheduling processes, as well as give technicians time to adopt new processes.
Then you can develop a comprehensive preventive maintenance program that includes other important assets and maybe even some advanced methods like condition-monitoring sensors and equipment.
Simplify preventive maintenance planning and scheduling with Sockeye
A well-executed preventive maintenance program can save you time, money, and headaches by reducing downtime and extending equipment life. But managing all the tasks and schedules can get complicated — and this is where Sockeye comes in.
Sockeye simplifies scheduling by:
- Connecting to your CMMS and helping you organize maintenance plans for all your assets.
- Automating PM task scheduling, whether calendar-based or usage-based.
- Balance PM scheduling with reactive work based on available work hours.
- Tracking maintenance progress and performance in real-time.
- Providing easy-to-use tools for reporting and optimizing your preventive maintenance plans and schedules.
With Sockeye, maintenance teams can stay ahead of equipment issues, streamline their workflows, and focus on what really matters: keeping your facility running smoothly.
Want to see how Sockeye can help your team? Schedule a demo with our team or reach out with any questions you might have.